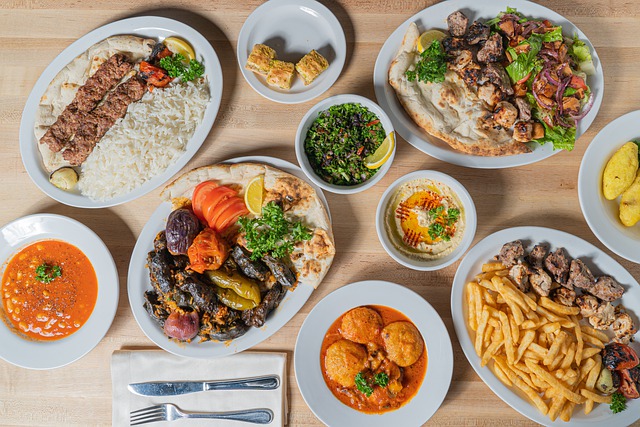
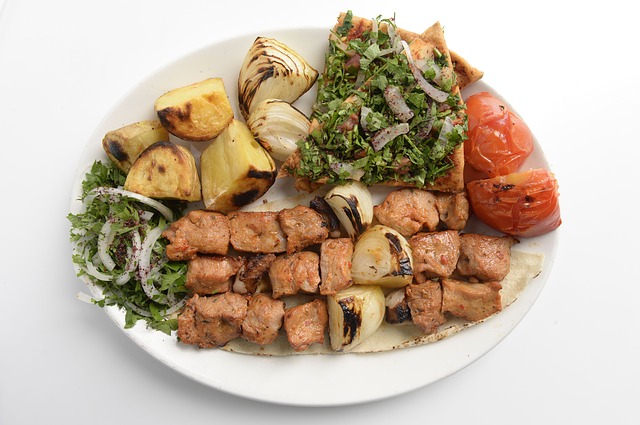
Is Middle Eastern Food Healthy? Healthy Middle Eastern Food
First, is middle eastern food healthy? YES!
Middle Eastern cuisine is one of the healthiest since it incorporates lean proteins, healthy fats, vegetables, and grains into almost every dish. It distinguishes itself from European cuisines through the use of rich spices, seeds, and herbs, particularly za’atar and cumin.
Please continue reading as I provide more detailed information about whether or not Middle Eastern food is healthy.
Table of Contents
Why Is Meed From The Middle East Healthy?
Characteristics
Olive oil, fish, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are emphasized as the main foods in both the Middle Eastern and Mediterranean diets. Red meat, dairy products, and sweets are only consumed in moderation on this kind of diet. This type of diet is extremely low in both saturated fat and cholesterol because they are only found in foods made from animal sources. Instead, the main sources of fat are heart-healthy fats like the monounsaturated and omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and olive oil. On this diet, fish and legumes, rather than red meat or poultry, are the sources of protein.
Coronary Health
The effects of the Middle Eastern/Mediterranean diet on your heart are its main advantage. Less consumption of saturated fats is caused by a decrease in meat and other animal products. The American Heart Association reported on the Lyon Diet Heart Study, which examined how diet affected the health of people who had already had a heart attack’s coronary system. There were two groups of patients: a A prudent diet or a diet in the Mediterranean style. Compared to prudent dieters, those following the Mediterranean diet consumed less animal products and saturated fat. According to the findings, those who ate a Mediterranean-style diet had a 50–70% lower risk of experiencing a second cardiovascular event.
Overall Health
A Middle Eastern diet can also improve brain function, cognitive function, and overall mortality. An investigation into the general health advantages of a Mediterranean diet was published in the “British Medical Journal” in 2008. The effects of a Mediterranean diet on mortality, Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and heart disease in 1.5 million people were examined in 12 studies that were the subject of this review. In accordance with this study, a Mediterranean-style diet can lower your risk of developing Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s disease as well as overall mortality, mortality from cancer or heart disease, and mortality from all causes.
Sample Meal Plan
If you eat a Middle Eastern-style diet, you might have a bowl of oats with sliced almonds as a garnish for breakfast. You might have a whole wheat roll on the side and a fresh, leafy green salad with tuna on top and a dressing made of olive oil and vinegar for lunch. Enjoy a pita-wrapped falafel sandwich for dinner with cucumber, beets, lettuce, tomatoes, and tahini on top.

Read about: Is Angel Food Cake Healthier?
Healthy Middle Eastern Food
Shawarma
One of the most popular traditional Middle Eastern dishes is shawarma, which can be found in almost all Middle Eastern restaurants. You’ll be hooked after taking the first bite of the meal because it is ridiculously delicious.
Due to the way the meat is prepared and roasted, this is one meal that is rarely made at home. It starts with a sizable, seasoned piece of meat that is roasting on a vertical rotisserie or spit that is slowly rotating. In recent years, other meats, such as beef, chicken, turkey, or veal, have also been used to make shawarma cones, which are typically made from lamb or mutton.
An extremely sharp butcher’s knife will be used by the waiter to slice off thin pieces of the tender meat as it roasts and place them on a sizable plate. You can order it as a snack on its own or as part of a dinner platter that also includes fries, hummus, falafel, tabbouleh, and possibly flatbread.
Hummus
One of the most adaptable Arab dishes is hummus, which is arguably the most popular food in the Middle East. It works well as a sandwich spread, a salad dressing base, and a variety of dips for foods like bread, vegetables, and falafel.
A bowl of hummus, generously drizzled with olive oil, and flatbread or pita are typically brought to the table when you order hummus as a side dish or appetizer in a restaurant.
The basic components of hummus are cooked chickpeas, olive oil, lemon juice, garlic, and tahini (sesame seed paste). If you live in Europe or North America, you can locate it in the refrigerated section of many supermarkets. Additionally, making it at home in a food processor or blender is very straightforward.
There are many different ways to make hummus, including red pepper, black olives, and garlic.
It’s challenging to top hummus when it comes to healthy middle eastern recipes. Protein, fiber, and iron are all abundant in chickpeas. Olive oil also has a lot of monounsaturated fat, which is good for the heart. See more about Is Ethiopian Food Healthy?
Falafel
A staple of Middle Eastern cuisine, falafel can be found in almost every restaurant serving that cuisine. It is typically served as a sandwich in a flatbread or pita wrap with tahini, hummus, or tzatziki on top.
It starts with dried chickpeas or fava beans that have been ground into a meal and then soaked. It is also known as felafel. The mixture is spiced with cumin, coriander, parsley, and spices like garlic and onion before being formed into a patty or ball and deep-fried until golden brown.
Falafel is a high-protein food, much like hummus. It also contains a lot of soluble fiber, which is thought to help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol.
Shakshouka
When making shakshouka, tomatoes, spices, and herbs are simmered slowly before eggs are cracked into the hot mixture and allowed to cook with the residual heat. As a result, eggs in a hot tomato sauce make a satisfying meal.
One of the best one-pot skillet dishes on the planet, this is very simple to make. Shakshouka is a typical breakfast food, but it’s also frequently eaten for lunch or dinner.
Mejadra
Mejadra, a type of pilaf, is one of the best comfort foods. The dish is prepared by cooking rice and lentils together, then adding a variety of spices, including a lot of cumin. A fragrant mixture is created, and to give the lentil and rice dish a crunchy contrast, fried onions are added on top.
Tabouleh
One of the best sides from the Middle East is tabouleh. If you’re looking for low-fat vegetarian food, this is the best option, so long as gluten isn’t a problem. It is also known as tabouli. It offers a full range of bold flavors.
Tomato, bulgur, spring onions, parsley, and mint are combined to make the dish. It’s final lemon juice and olive oil dressing is what gives it its customary deliciousness.
Try tabouleh if you want to experience the flavorful cuisine of the Middle East. The food is rich in dietary fiber, low in saturated fats, high in vitamins and minerals, and offers a good amount of vitamins and minerals. By doing so, you can lower your risk of cardiovascular disease and maintain a strong immune system.
Labneh
The most healthful Lebanese food is likely labneh, a staple of mezze made from cow’s milk. This soft cheese will probably win your heart if you’re looking for a flavorful, energizing, and adaptable Middle Eastern dish.
Labneh is actually a type of yogurt cheese. Although it is prepared to resemble the thickest Greek yogurt, it is neither tart nor sour in flavor.
Despite having a Lebanese origin, labneh is now a global food that enjoys great popularity and dominance. For a wholesome breakfast or a tasty lunch, spread this food on some fresh pita and serve it with some olive oil.
One of the best probiotic foods, labneh contains a variety of beneficial bacteria that will strengthen your immune system. It has a high protein content, few calories, and is remarkably beneficial to your health.
Conclusion
So, is middle eastern food healthy?
Similar to their European counterparts, Middle Eastern food contains ingredients that are healthy fats. Saturated and trans fats, which are linked to heart disease, are substituted with them in food. Similar to the Mediterranean diet, the main source of fat in Middle Eastern food is olive oil. Low-density lipoprotein, also known as “bad” cholesterol, is known to be decreased in the body by monounsaturated fat, which is present in olive oil. Nuts and seeds, which Arabs love to consume on a daily basis, are another source of monounsaturated fats.
I appreciate your reading.